Sharding
Sharding
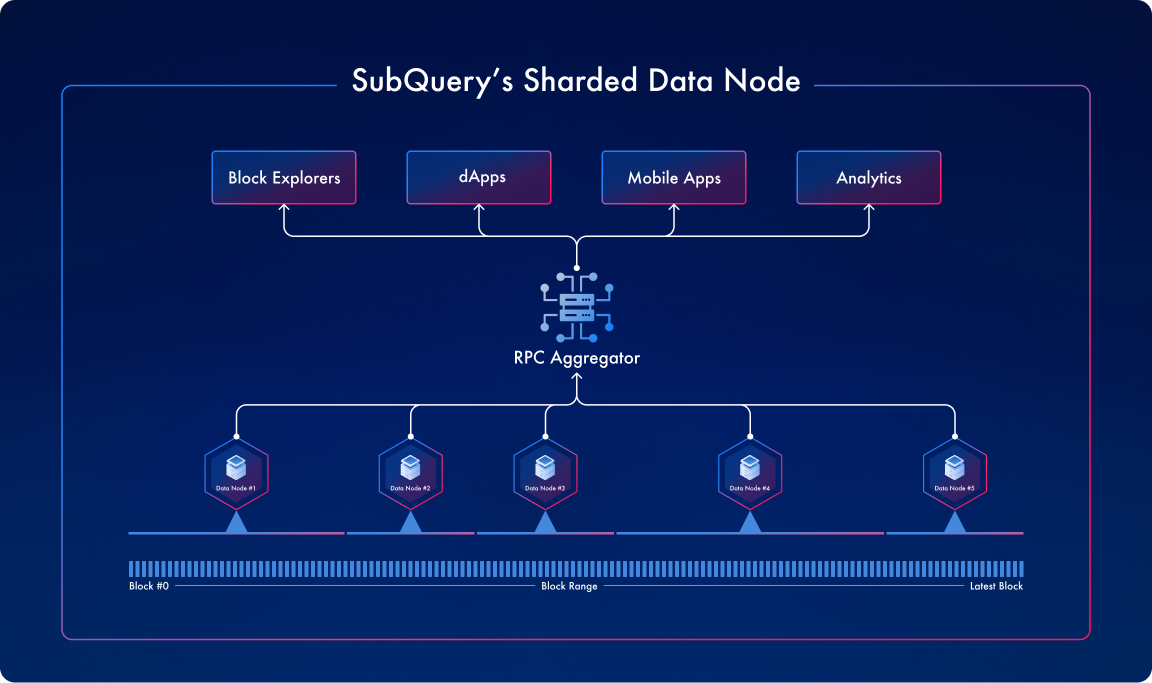
Sharding allows you to take a subset of the chain, this reduces storage requirements to run a node an serve data on the SubQuery Network. The Sharded Data Node builds on the SubQuery Data Node, an enhanced and heavily-forked RPC node (starting with the Geth client) that is perfectly optimised for querying, especially on endpoints like eth_getLog. Further, it will have the ability for clients to filter transactions in a single RPC call.
It is recommended to confirgure the shard range using CLI flags or config as adjusting the range can take some time to remove data and the RPC methods can time out.
Background
The SubQuery Sharded Data Node, herein referred to as Sharded Data Node, represents a novel category of chain nodes, developed and maintained by the SubQuery team, for various network clients, starting from Geth. The purpose of these nodes is to develop a more performant RPC that is easily decentralised, and while doing this we realised that this novel solution would also help solve the problems raised by EIP-4444.
The foundational objective of Sharded Data Node is to offer an economically efficient and more performant alternative to conventional archival RPC nodes, enabling operation on lower-specification machines, requiring less storage, and thereby facilitating decentralisation away from dominant entities.
Set Head
Behaviour
The head of the shard can be set to any height that is greater than the tail height of the same shard. If it is set to a height before the current chain height, the node will sync up to that height.
If the head is set to a hight to number greater than the latest height it will sync until the chain reaches that height. The height can be unset with null or 0, this will start syncing to the latest height.
Warning
In order to set the head to an earlier block, chain state is required at the desired height. An error will be thrown if a height is set where there is no state.
Config
On startup you can set the config via -shardend=<block-number>
Or via the admin RPC:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "admin_setEndHeight",
"params": [<block-number>],
"id": 0
},This will return true if successful otherwise an error.
Example
curl -X POST --data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"admin_setEndHeight","params":[20000],"id":1}'Example response
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": true
}Set Tail
Behaviour
The tail of the shard can be set to any height that is greater than the current tail and less than the head. It cannot be set to a future block and must first be synced.
Config
On startup you can set the config via -shardstart=<block-number>.
Or via the admin RPC:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "admin_setStartHeight",
"params": [<block-number>],
"id": 0
},This will return true if successful otherwise an error.
Example
curl -X POST --data '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"admin_setStartHeight","params":[20000],"id":1}'Example response
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": true
}Config
To get the curent shard config you can use the following admin RPC:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "subql_dataInfo",
"params": [],
"id": 0
},This will return a json object with the current config
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"desiredChainDataStart": 20,
"desiredChainDataEnd": 90
}
}State
Setting the tail doesn't modify the chain state, this needs to be done manually. To do this please follow the go ethereum docs on sharding.
Warning
Pruning the state requires access to the state root for a block, if the block has been removed from the chain then the state root will need to be sourced from elsewhere.
Other information
- The genesis block is never removed, it is needed to ensure the node runs
- SubQuery data node methods will be limited to the range of the tail and head
