Install Node Operator Service on Linux
Install Node Operator Service on Linux
Let's see how to run the Node Operator Service on a cloud provider.
Run Node Operator Services on Cloud Linux Instance
We will use a Linux EC2 instance from AWS in the following examples.
Note
Note: You can use any other cloud providers, we will try our best to provide support and troubleshooting help.
Step 1 - Launch a Virtual Machine
There are plenty of online guides on how to launch a compute engine on various cloud providers, including AWS, GCP, Azure, Digital Ocean etc. You can follow this tutorial to launch a new EC2 on AWS (we recommend a compute engine equivalent to a t3.medium linux EC2)
Step 2 - Install Docker and Docker-Compose
- SSH access to the EC2 instance:
ssh -i key_file.pem ec2-user@ec2-34-204-200-76.compute-1.amazonaws.comImportant
Please change the default PostgreSQL password in the POSTGRES_PASSWORD field and in the coordinator-service's postgres-password field. Replace it with your own one.
Pay attention to the postgres version. The latest version is postgres:17-alpine. You should not change the postgres version when it is running stable, changing will cause errors. Upgrading the version requires some advanced techniques such as postgres upgrade or backup, restore.
- Then, install Docker and set auto start:
sudo yum install docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker- Note that you need to install the docker-compose command tool in EC2, in order to use the docker-compose features:
# get the latest version for docker-compose
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest/download/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m) -o /usr/bin/docker-compose
# fix permissions after download:
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/docker-compose
# verify the installation
sudo docker-compose versionStep 3 - Download the Docker Compose File for Node Operator Services
Run the following command:
mkdir subquery-indexer && cd subquery-indexer
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/subquery/network-indexer-services/main/deploy/docker-compose.yml -o docker-compose.ymlImportant
Please change the POSTGRES_PASSWORD in postgres and postgres-password in coordinator-service to your own one
Step 4 - Start Node Operator Services
Run the service using the following command:
sudo docker-compose up -dIt will start the following services:
indexer_dbindexer_coordinatorindexer_proxyindexer_cache
Note
Each project you start indexing will create 2 extra containers node_qm---------- and query_qm---------- that has the 15 first characters of the project's Qm-hash.
Now, check the service status:
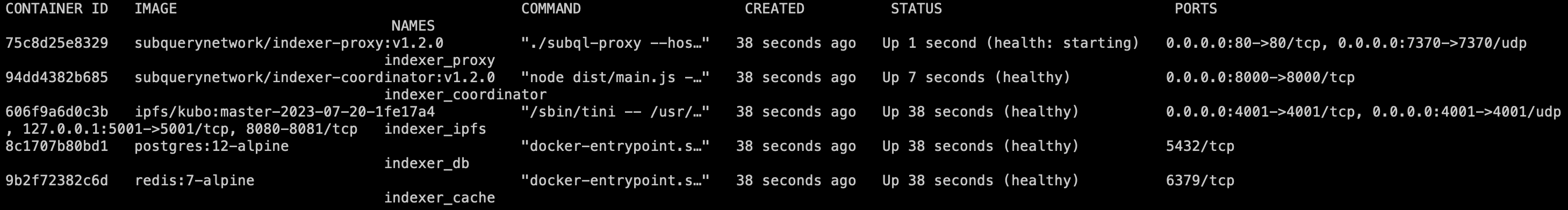
Step 5 - Set Up Auto Start
Create /etc/systemd/system/subquery.service.
[Unit]
Description="SubQuery systemd service"
After=network.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=0
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=10
User=root
SyslogIdentifier=subquery
SyslogFacility=local7
KillSignal=SIGHUP
WorkingDirectory=/home/ec2-user/subquery-indexer
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker-compose up -d
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetRegister and start the service by running:
systemctl enable subquery.service
systemctl start subquery.serviceAfter that, verify that the service is running:
systemctl status subquery.serviceAdvanced Settings
Docker Log Rotating
If you've done the above setup, you surely see everything is running in docker, both Node Operator services and subquery jobs. With the time going, log will swallow a huge of your local disk and you may have to stop the service to clean it up.
To avoid running into this situation, you can do the following settings.
1. Change log driver to journald
Depends how you install docker on your server, you may find your docker config in /etc/docker/daemon.json or /var/snap/docker/<version>/config/daemon.json
Open it and add log-driver settings
{
...
"log-driver": "journald"
}then restart docker.
2. setup journald log rotate
Add space limit to journald by set up SystemMaxUse and RuntimeMaxUse
Next Steps
You have successfully installed and started the Node Operator Service on Linux, please return to the previous page
Tip
Having trouble running a command or setting up the service? Got stuck in the process? Find your solutions here.
